
Saswat Patra; Neha Gupta
The study examines the relationship between volume and volatility in leading cryptocurrencies i.e. Bitcoin and Ethereum, within the framework of Mixture of Distribution Hypothesis (MDH). It accommodates structural shifts in the cryptocurrency prices and uses fat-tailed distributions. The results show that the MDH is rejected for both cryptocurrencies, and volume alone cannot explain the heteroskedasticity of returns; however, it acts as a significant predictor for volatility, especially when incorporating structural breaks in the model. Further, the forecasting performance improves when fat-tailed distributions, such as the skewed student’s t and Johnson’s Su distribution are used to model the innovations. Thus, volume holds important information in the crypto markets and can affect returns, thereby, raising concerns about market efficiency. Our results are robust across different periods, modelling approaches and forecasting horizons, and hold substantial implications for traders, market participants, regulators, and governments in designing effective policies.
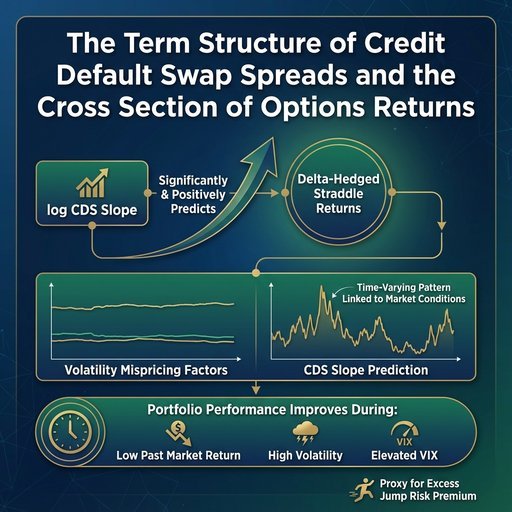
Hao Zhang, Yukun Shi, Dun Han, Pei Liu, Yaofei Xu
This paper, using the natural logarithmic form credit default swap (log CDS) slope, examines the variation in cross‐sectional 1‐month ATM delta‐hedged straddle returns. Our analysis reveals that the log CDS slope significantly and positively predicts these returns, even when accounting for several key volatility mispricing factors. Further investigation shows that this predictive relationship exhibits a strong time‐varying pattern, closely linked to market conditions. In contrast, the relationship between notable volatility mispricing factors and straddle returns remains relatively stable over time. Constructing a long‐short quintile portfolio on straddle options confirms that trading performance improves when the past 12‐month market return is at a historically lower level, market volatility is at a historically higher level, and the VIX is elevated. Log CDS slope, as a proxy for excess jump risk premium, significantly predicts delta‐hedged option returns during periods of high volatility.
Albert J. Menkveld, Anna Dreber, Felix Holzmeister, Juergen Huber, Magnus Johannesson, Michael Kirchler, Sebastian Neusüß, Michael Razen, Utz Weitzel, Fincap Team, Fearghal Kearney, Tony Klein, Liangyi Mu, and others
In statistics, samples are drawn from a population in a data-generating process (DGP). Standard errors measure the uncertainty in estimates of population parameters. In science, evidence is generated to test hypotheses in an evidence-generating process (EGP). We claim that EGP variation across researchers adds uncertainty--nonstandard errors (NSEs). We study NSEs by letting 164 teams test the same hypotheses on the same data. NSEs turn out to be sizable, but smaller for more reproducible or higher rated research. Adding peer-review stages reduces NSEs. We further find that this type of uncertainty is underestimated by participants.

Arbab K. Cheema, Arman Eshraghi, Qingwei Wang
Stock price synchronicity is a critical consideration for asset allocation, risk assessment, and hedging decision. We present novel evidence that individual stock returns comove more persistently on certain days of the week. Specifically, we show that release of macroeconomic news on Mondays, which typically see fewer announcements, leads to such stronger comovement, and that this is distinct from the Monday effect typically discussed in the literature. This synchronicity is more pronounced among large, old and low volatility firms, in both up- and down-market conditions. We argue this effect is partly due to 'simultaneous contrast', i.e., perception of stimulus depending on its surrounding environment. Monday announcements have a larger impact just as thunder in a quiet night sounds louder. Our findings are robust after controlling for day-of-the-week effects, economic uncertainty, risk aversion, investor sentiment, short-selling constraints and proxies for attention to news.

Xiaohang Ren, Yuxuan Cao, Pei Liu, Dun Han
Using 2663 Chinese A-share listed companies from 2003 to 2019, we investigate the relationship between geopolitical risk (GPR) and firm idiosyncratic volatility through panel fixed effects and attempt to explain the mechanism. The main findings are presented as follows. First, GPR can explain the change of firms' idiosyncratic volatility. Different industry conditions and ownerships have heterogeneous effects on the firms' idiosyncratic volatilities. In addition, the interaction terms of ownership concentration, competitive intensity and operating leverage with GPR are statistically significant, and they interact with GPR to affect firms' idiosyncratic volatility. After we conduct a series of robustness tests using methods such as instrumental variables, we innovatively introduce the South China Sea dispute as an external event and use the DID (Difference-in-difference) model to analyze the impact of geopolitical events on corporate risk-taking, our findings remain valid. Our research contributes to a better understanding of geopolitical risk and firms' idiosyncratic volatility.
Minyou Fan, Fearghal Kearney, Youwei Li, Jiadong Liu
Recent literature shows that momentum strategies exhibit significant downside risks over certain periods, called momentum crashes. We find that high uncertainty of momentum strategy returns is sourced from the cross-sectional volatility of individual stocks. Stocks with high realised volatility over the formation period tend to lose momentum effect. We propose a new approach, generalised risk-adjusted momentum (GRJMOM), to mitigate the negative impact of high momentum-specific risks. GRJMOM is proven to be more profitable and less risky than existing momentum ranking approaches across multiple asset classes, including the UK stock, commodity, global equity index, and fixed income markets.

Dun Han, Liyan Han, Yanran Wu, Pei Liu
We study dividend fund buying behavior using over 80,000 individual Chinese mutual fund investors from a private Chinese mutual fund account dataset. Based on a variety of specifications and logistic regressions, we empirically investigate investors' characteristics in choosing dividend-paying and/or growth mutual funds under different market scenarios. To the best of our knowledge, this research represents an initial attempt to study individual dividend investors in mutual fund markets. We find that older Chinese investors prefer dividend-paying funds less than growth funds, but this depends on different market conditions, and the age effect shows a nonlinear mode when considering age grouping. Moreover, investors' prior experience plays a crucial role in choosing the fund type; however, the conclusions vary with market scenarios. In addition, female investors prefer more dividend-paying funds than do male investors, but investing experience counteracts this difference. We also find that geographic location is a contributor when investors decide the fund type.


